
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
2 Quanzhou San’an Integrated Circuit Co., Ltd., Quanzhou 362300, China
3 Eastern Institute of Technology, Ningbo 315200, China
Surface acoustic wave (SAW) resonators based on lithium tantalate (LT, ) wafers are crucial elements of mobile communication filters. The use of intrinsic LT wafers typically brings about low fabrication accuracy of SAW resonators due to strong UV reflection in the lithography process. This hinders their resonance frequency control seriously in industrial manufacture. LT doping and chemical reduction could be applied to decrease the UV reflection of LT wafers for high lithographic precision. However, conventional methods fail to provide a fast and nondestructive approach to identify the UV performance of standard single-side polished LT wafers for high-precision frequency control. Here, we propose a convenient on-line sensing scheme based on the colorimetry of reduced Fe-doped LT wafers and build up an automatic testing system for industrial applications. The levels of Fe doping and chemical reduction are evaluated by the lightness and color difference of LT-based wafers. The correlation between the wafer visible colorimetry and UV reflection is established to refine the lithography process and specifically manipulate the frequency performance of SAW resonators. Our study provides a powerful tool for the fabrication control of SAW resonators and will inspire more applications on sophisticated devices of mobile communication.
Photonics Research
2024, 12(2): 341

Wenyun Du 1,2Meiping Zhu 1,2,3,4,*Jun Shi 1,2,3Tianbao Liu 1,2[ ... ]Jianda Shao 1,2,3,4
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laboratory of Thin Film Optics, Key Laboratory of Materials for High Power Laser, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
3 Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, China
4 CAS Center for Excellence in Ultra-intense Laser Science, Shanghai, China
The laser-induced damage threshold (LIDT) of plate laser beam splitter (PLBS) coatings is closely related to the subsurface absorption defects of the substrate. Herein, a two-step deposition temperature method is proposed to understand the effect of substrate subsurface impurity defects on the LIDT of PLBS coatings. Firstly, BK7 substrates are heat-treated at three different temperatures. The surface morphology and subsurface impurity defect distribution of the substrate before and after the heat treatment are compared. Then, a PLBS coating consisting of alternating HfO2–Al2O3 mixture and SiO2 layers is designed to achieve a beam-splitting ratio (transmittance to reflectance, s-polarized light) of approximately 50:50 at 1053 nm and an angle of incidence of 45°, and it is prepared under four different deposition processes. The experimental and simulation results show that the subsurface impurity defects of the substrate migrate to the surface and accumulate on the surface during the heat treatment, and become absorption defect sources or nodule defect seeds in the coating, reducing the LIDT of the coating. The higher the heat treatment temperature, the more evident the migration and accumulation of impurity defects. A lower deposition temperature (at which the coating can be fully oxidized) helps to improve the LIDT of the PLBS coating. When the deposition temperature is 140°C, the LIDT (s-polarized light, wavelength: 1064 nm, pulse width: 9 ns, incident angle: 45°) of the PLBS coating is 26.2 J/cm2, which is approximately 6.7 times that of the PLBS coating deposited at 200°C. We believe that the investigation into the laser damage mechanism of PLBS coatings will help to improve the LIDT of coatings with partial or high transmittance at laser wavelengths.
laser-induced damage threshold nodule defect plate laser beam splitter subsurface impurity defect High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2023, 11(5): 05000e61
1 上海市生态气象和卫星遥感中心,上海 200030
2 国家卫星气象中心 中国气象局中国遥感卫星辐射测量和定标重点开放实验室 许健民气象卫星创新中心,北京 100081
我国风云四号A星(FY-4A)携带高光谱红外干涉式大气探测仪(Geostationary Interferometric Infrared Sounder,GIIRS)首次实现了地球静止轨道红外高光谱探测,可连续获得大气温湿度廓线信息。基于常规无线电探空资料,从产品的探测能力和精度方面对2020年FY-4A/GIIRS大气温度廓线产品开展质量评估,为产品应用和算法研究提供参考。结果表明:FY-4A/GIIRS反演大气温度廓线探测能力在高度层次和月份统计上受云活跃度影响较大;晴空条件下大气整层均方根误差约为2 K,700~1 000 hPa的大气低层较大,约2.5 K,偏差整层以负值为主;月尺度质量评估可见夏秋两季明显优于冬春季,有利于灾害性天气多发季节的监测;有云条件下单个像元的温度廓线误差显著增大,采用多像元Cressman客观分析可有效提高产品可用性;低海拔地区温度廓线产品质量整体优于高海拔地区,可极大地弥补我国东部、南部地区以及广阔的洋面上的探空资料的不足。
高光谱 质量评估 温度廓线 FY-4A/GIIRS 无线电探空 hyperspectral quality evaluation temperature profile FY-4A/GIIRS radiosonde 
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Chongqing, China
2 Research Center of Laser Fusion, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang, China
3 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology and Systems, Ministry of Education, Chongqing University, Chongqing, China
In this study, a toroidal quartz ( $20\overline{2}3$ ) crystal is designed for monochromatic X-ray imaging at 72.3°. The designed crystal produces excellent images of a laser-produced plasma emitting He-like Ti X-rays at 4.75 keV. Based on the simulations, the imaging resolutions of the spherical and toroidal crystals in the sagittal direction are found to be 15 and 5 μm, respectively. Moreover, the simulation results show that a higher resolution image of the source can be obtained by using a toroidal crystal. An X-ray backlight imaging experiment is conducted using 4.75 keV He-like Ti X-rays, a 3 × 3 metal grid, an imaging plate and a toroidal quartz crystal with a lattice constant of 2d = 0.2749 nm. The meridional and sagittal radii of the toroidal α-quartz crystal are 295.6 and 268.5 mm, respectively. A highly resolved image of the microgrid, with a spatial resolution of 10 μm, is obtained in the experiment. By using similar toroidal crystal designs, the application of a spatially resolved spectrometer with high-resolution X-ray imaging ability is capable of providing imaging data with the same magnification ratio in the sagittal and meridional planes.
dynamic diffraction monochromatic X-ray imaging resolution toroidal quartz crystal High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2022, 10(6): 06000e37

Tianbao Liu 1,2Meiping Zhu 1,2,3,4,*Wenyun Du 1,2Jun Shi 1,2,3[ ... ]Jianda Shao 1,2,3,4
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laboratory of Thin Film Optics, Key Laboratory of Materials for High Power Laser, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
3 Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, China
4 CAS Center for Excellence in Ultra-intense Laser Science, Shanghai, China
5 CREOL, College of Optics and Photonics, University of Central Florida, Orlando, USA
Various coatings in high-power laser facilities suffer from laser damage due to nodule defects. We propose a nodule dome removal (NDR) strategy to eliminate unwanted localized electric-field (E-field) enhancement caused by nodule defects, thereby improving the laser-induced damage threshold (LIDT) of laser coatings. It is theoretically demonstrated that the proposed NDR strategy can reduce the localized E-field enhancement of nodules in mirror coatings, polarizer coatings and beam splitter coatings. An ultraviolet (UV) mirror coating is experimentally demonstrated using the NDR strategy. The LIDT is improved to about 1.9 and 2.2 times for the UV mirror coating without artificial nodules and the UV mirror coating with artificial nodule seeds with a diameter of 1000 nm, respectively. The NDR strategy, applicable to coatings prepared by different deposition methods, improves the LIDT of laser coating without affecting other properties, such as the spectrum, stress and surface roughness, indicating its broad applicability in high-LIDT laser coatings.
coating electric-field enhancement laser-induced damage threshold nodule defect nodule dome removal High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2022, 10(5): 05000e30
1 重庆大学光电技术及系统教育部重点实验室, 重庆 400044
2 重庆邮电大学光电工程学院, 重庆 400065
3 中国工程物理研究院激光聚变研究中心, 四川 绵阳 621900
提出采用球面弯曲晶体作为透射式成像器件的硬X射线成像系统,其基本结构是一个具有各向同性的X射线点源和一个球面Laue透射晶体,该结构能够解决常用反射式晶体结构不易实现能量在8 keV及以上的硬X射线成像的难题。在成像系统中,X射线由微小点源辐射,经过置于球面晶体前面的成像网格物体后,由α-石英球面晶体透射,最后成像于晶体后方的检测器面上。讨论了球面透射晶体获取不同放大倍率图像的成像机理,利用射线追迹程序设计透射成像系统进行仿真。模拟结果表明,所提结构能够实现二维空间分辨成像。铜靶X射线管背光成像实验也证明实验结果与理论分析具有一致性。
光学学报
2022, 42(11): 1134011
1 重庆邮电大学光电工程学院, 重庆 400065
2 重庆大学光电技术及系统教育部重点实验室, 重庆 400044
3 中国工程物理研究院激光聚变研究中心, 四川 绵阳 621900
基于晶体衍射的X射线诊断技术是大型激光装置及同步辐射装置上X射线光谱学诊断、材料分析与结构表征等研究领域中获取关键状态参数的重要技术手段。基于动力学衍射理论的晶体衍射效率计算分析与基于不同面型晶体的谱仪结构设计是X射线晶体谱仪的两大基础研究方向。对X射线动力学衍射理论等经典晶体衍射理论、不同晶体对象衍射计算方法的发展来由和最新进展进行了总结讨论;对不同结构X射线晶体谱仪的衍射聚焦特性、发展及应用进行了讨论;综合阐述X射线晶体谱仪涉及的X射线晶体衍射理论及各种谱仪衍射聚焦特性方面的创新点和进步点以及总体发展态势。
光学学报
2022, 42(11): 1134008
光子学报
2021, 50(11): 1128002
1 重庆邮电大学光电工程学院, 重庆 400065
2 重庆大学光电技术及系统教育部重点实验室, 重庆 400044
3 中国工程物理研究院激光聚变研究中心, 四川 绵阳 621900
针对等离子体X射线成像诊断高空间分辨率的需求,本文提出了一种基于超环面石英晶体衍射聚焦元件的钛靶X射线高分辨率聚焦成像结构,研究分析了超环面晶体成像的原理及特性。为证明超环面晶体具有高空间分辨率特性,基于X射线衍射追迹原理对球面及超环面晶体的X射线衍射进行性能仿真,在保持射线源及成像物体不变的条件下,对比分析了不同晶体面形结构的衍射成像结果,计算得到球面晶体和超环面晶体在弧矢方向上的成像空间分辨率分别约为40 μm和5 μm。仿真结果表明超环面晶体作为X射线衍射分光元件较传统的球面晶体具有强聚焦、高空间分辨率的特点,是较为理想的X射线衍射分光元件。此外,本文利用特征峰能量为4.75 keV的钛靶激光装置、IP板以及超环面石英晶体完成了X射线背光成像实验研究,其中超环面石英晶体的子午面和弧矢面半径分别为295.6 mm和268.5 mm,晶格常数2d=0.2749 nm,实验获得了清晰的栅格成像图。实验结果表明该超环面石英晶体能够对钛靶X射线进行衍射成像,并能获得较高的成像空间分辨率。实验中获得的超环面石英晶体衍射的最终成像空间分辨率为10 μm。
材料 超环面石英晶体 X射线衍射 聚焦 成像空间分辨率 中国激光
2021, 48(21): 2103002
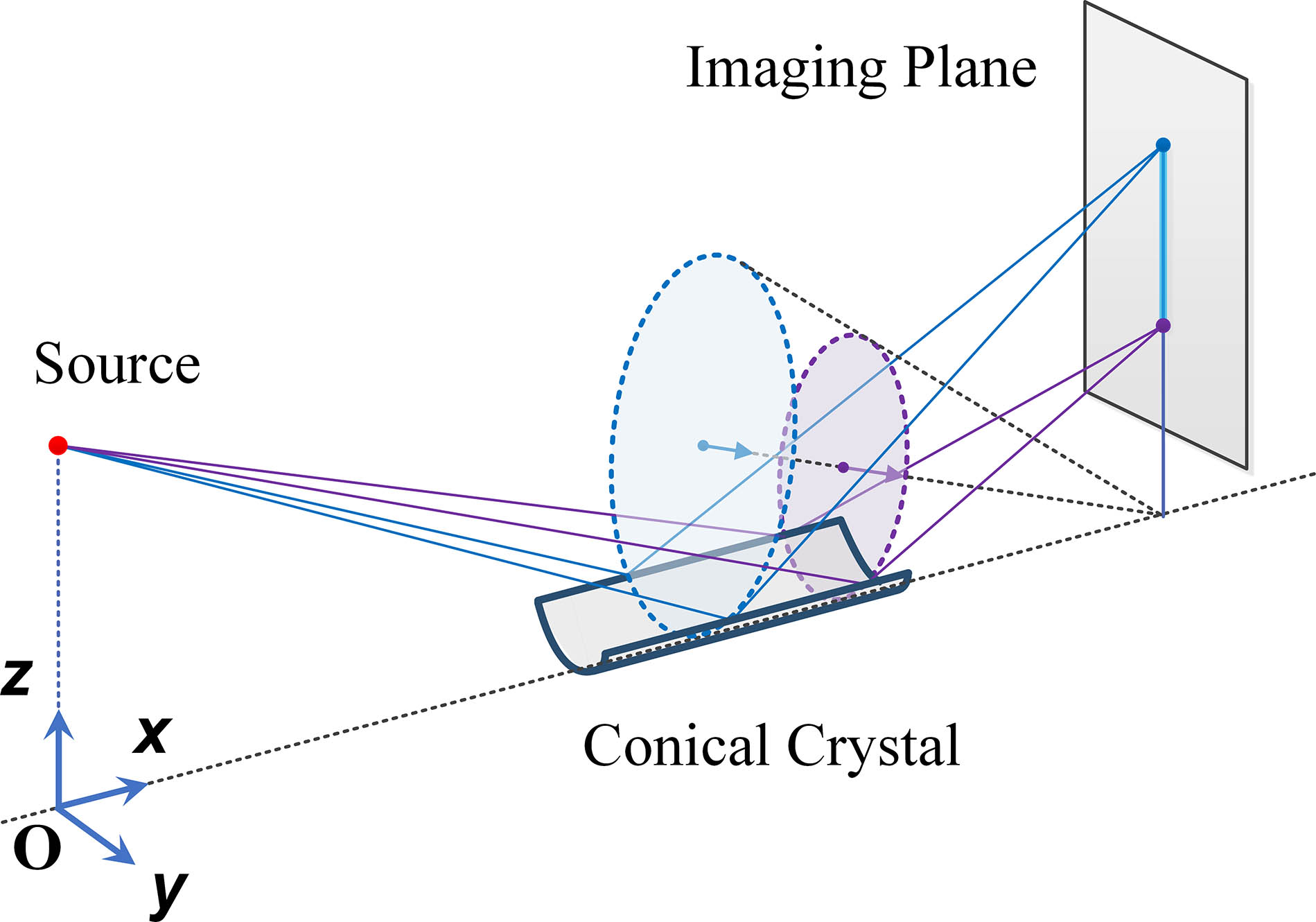
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology and Systems of the Ministry of Education, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
2 College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Chongqing 400065, China
3 Research Center of Laser Fusion, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang 621900, China
In spectral diagnostic physics experiments of inertial confinement fusion, the spectral signal is weak due to the low diffraction efficiency when using bent crystals. A spectral diagnostic instrument with high efficiency and wide spectral range is urgently needed. A multi-curvature bent crystal with multi-energy focusing ability is proposed based on the traditional conical crystal geometry. It has advantages of wide spectral range, strong focusing ability, and high spectral resolution. It also can eliminate the imaging aberration in principle due to rotational symmetry for the incoming X rays. A spectral diagnostic experiment based on a fabricated multi-curvature α-quartz crystal was accomplished using a titanium X-ray tube of the bent crystal, and the corresponding experimental data using a plane α-quartz crystal was also acquired to demonstrate the strong focusing ability. The result shows that the Kα intensity of the multi-curvature α-quartz crystal is 157 times greater than that of the plane crystal, and the corresponding energy range is about 4.51–5.14 keV. This diagnostic instrument could be combined with a streak camera at a vertical direction so as to intensify the diffracted X-ray signal with a wide spectral range.
inertial confinement fusion X-ray crystal spectrometer multi-curvature bent crystal X-ray diffraction Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(11): 113401





